In this article we will discuss about:- 1. Introduction to Carp Culture 2. Basic Principles of Carp Culture 3. Criteria for Selection of Fishes 4. Composite Fish Farming in India 5. Carp Culture Management: Improved Technique.
Indian major carps are:
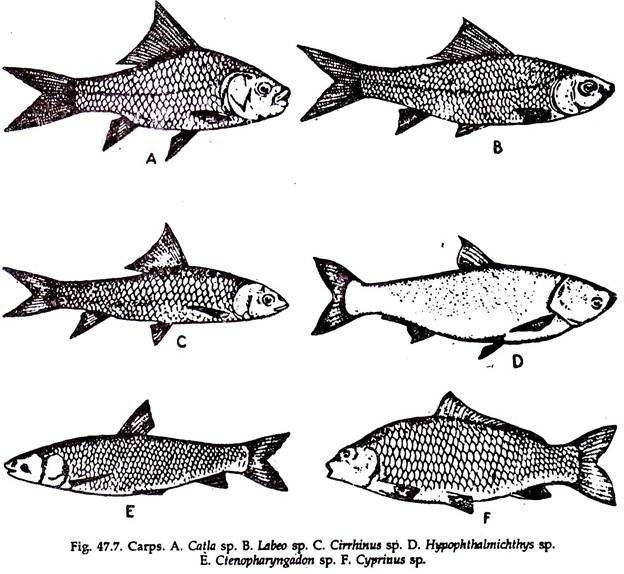
A. Catla (Catla Catla)
B. Rohu (Labeo rohita)
ADVERTISEMENTS:
C. Mrigal (Cirrhinus mrigal)
The popular exotic major carps are:
A. Cyprinus carp (Cyprinus carpio)
B. Silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix)
ADVERTISEMENTS:
C. Grass carp (Ctenopharyngadon idolla)
In present day carp culture, species of carps (Fig. 47.7) with different feeding habits and habitats are grown at a definite ratio in a pond to fully occupy the space and utilise available food. This is known as ‘composite fish culture’ or ‘mixed fish farming’ or ‘poly-culture’ or ‘intensive fish farming’. An average yield of 3,000 kilogram/ hectare/year has been obtained.
1. Catla and silver carp occupy the upper stratum of pond water. Catla feeds on zoop- lankton while silver carp is predominantly a phytoplankton feeder.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
2. Rohu and grass carp occupy middle stratum. Rohu feeds on small aquatic vegetation and grass carps mainly on soft aquatic macrophytes.
3. Mrigal and cyprinus carp occupy lower stratum of water and feed upon benthonic organisms and faeces of upper dwellers and other organic matters raining down.
Six species of carp, cultured at a time, may yield 3,000 to 9,000 kg/ha/yr.
Basic Principles of Carp Culture:
1. The use of fast-growing non-predatory food fishes, that effectively utilize both natural and supplementary fish food.
2. Use of compatible species—not competitors— for food and space.
3. Stocking of requisite number of each species with a total adequate population to properly utilize the whole water body and all food resources.
4. Increasing carrying capacity of the pond on its fish productive potential through the application of suitable manure and also increasing the stocking density by providing supplementary food.
5. Manipulation of the number of fishes in the course of culture through intermediate harvest.
Criteria for Selection of Fishes:
1. Plankton feeders; food chain being short, energy output is higher.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
2. Rapid growth rate.
3. Compatible, i.e., capable to live with other species of fishes.
4. Good looking and good to taste, i.e., marketable.
5. Non-predatory.
Composite Fish Farming in India:
Three combinations are adopted in composite fish culture in India.
The ideal combinations are:
A. Indian major carps alone:
a. Ratio—Catla 4: Rohu 3: Mrigal 3.
b. Density 3,750 fingerlings/ha.
c. The average weight attained 700 gm/
d. Yield varies with ratios and density and ranges from 1,400 to 3,000 kg/ha/yr.
B. Exotic carps alone:
Successfully introduced in 1957.
a. Ratio—Silver carp 3: Grass carp 1: Cyprinus carp 2.
b. Density 5,000/ha.
c. Yield 2,900—3,000 kg/ha/yr.
C. Indian and exotic carps together:
a. Ratio—Catla 1: Rohu 3: Mrigal 1.5: Silver carp 2: Grass carp 1: Cyprinus carp 1.5.
b. Density 5,000/ha.
c. Yield 6,000 kg/ha/yr.
Carp Culture Management: Improved Technique:
a. Use of ‘Mohua’ (Madhuka latifolia) oil cake to eradicate unwanted fishes and other aquatic organisms. It is initially a fish poison but turns to a good fertiliser after proper treatment
b. Use of both organic and inorganic manures, viz., cow dung and triple superphosphate.
c. Application of lime prior to the use of fertilizer.
d. Use of quality supplementary feed like ground nut oil cake, rice bran and aquatic weeds.
e. High stocking density 5,000 to 7,500 and even 10,000 fingerlings/ha.
f. Correct stocking ratio of fingerlings of different species.
g. Yield 8,000 to 9,000 kg/ha/yr.