The following points highlight the top seven characteristics of energy flow in an ecosystem. The characteristics are: 1. Unidirectional Flow of Energy 2. Progressive Decrease in Energy 3. Respiratory Loss High in Higher Trophic Levels 4. Higher Efficiency of Assimilation at Higher Trophic Level 5. Un-Utilised Energy 6. Energy Flow 7. The Cycling.
Characteristic # 1. Unidirectional Flow of Energy:
The most important characteristic is the one-way street along which energy flows. The energy that is captured by the autotrophs does not revert back to solar input; that which passes to the herbivores does not pass back to the autotrophs; and so on. The immediate implication of this unidirectional energy flow is that the ecosystem would collapse if the primary energy source, the sun, was cut-off.
Characteristic # 2. Progressive Decrease in Energy:
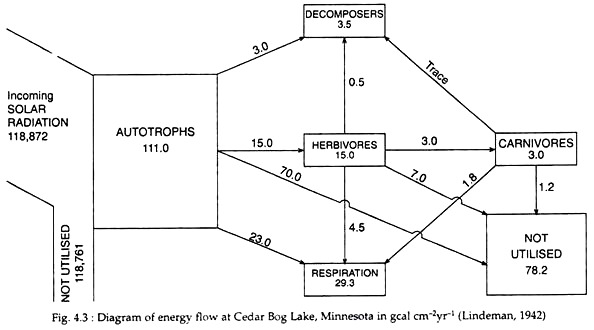
From Fig. 4.3 it is to be noted that at each trophic level there is progressive decrease in energy. This is because at the time of energy transfer from one trophic level to the other a substantial amount of energy is lost as it is dissipated as heat during metabolic activity.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Characteristic # 3. Respiratory Loss High in Higher Trophic Levels:
From the above case of Cedar Bog Lake it can be seen that, as we go higher up the food-chain, respiratory loss gets higher and higher. The respiratory loss in autotrophs is 21 percent, in herbivores 30
percent and in carnivores 60 percent. This higher energy loss in carnivores is due to its greater locomotory activity.
Characteristic # 4. Higher Efficiency of Assimilation at Higher Trophic Level:
As we go higher up the trophic level there is greater efficiency of energy assimilation. In the above example of Cedar Bog Lake, the efficiency of solar energy capture by the autotrophs is only 0.1 percent. From the autotrophs to herbivores it is 3.4 percent, and from herbivores to carnivores it is 28.6 percent.
Characteristic # 5. Un-Utilised Energy:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
In all ecosystems, despite the utilisation of energy in various metabolisms by different organisms, large amount of energy always remains in the system as standing crop. This indicates that the ecosystem is under-grazed.
Characteristic # 6. Energy Flow:
Energy flow in an ecosystem follows the first and second laws of thermodynamics. The energy flow through any trophic level equals the total assimilation at that level, which in turn, equals the production of biomass plus respiratory loss.
Characteristic # 7. The Cycling:
The cycling of mineral elements has been included in the energy flow diagram. Unlike energy, nutrients are typically regenerated and retained within the system.