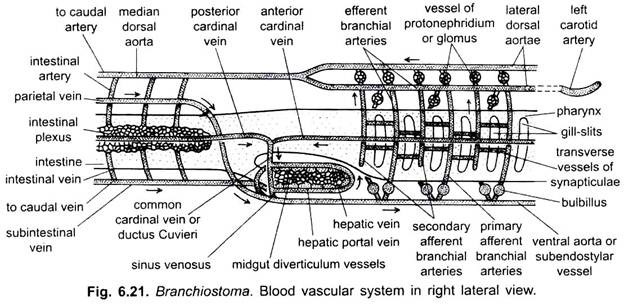
The blood vascular system of Branchiostoma is of closed type. The blood is colourless and devoid of corpuscles and respiratory pigment. Blood is found not only in blood vessels but also in lymph spaces, around fin-rays, and in metapleural folds. Its main function is to transport the food and excretory wastes.
Heart is not found in Branchiostoma. Most blood vessels are similar, but due to their homologies with blood vessels of vertebrates they are called arteries or veins. The principal arteries have muscular walls and only dorsal aorta has an endothelial lining.
Sinus Venosus:
It is a thin-walled sac below the hind end of pharynx. It is formed by the union of numerous vessels (veins) which collect blood from the entire body. It anteriorly leads into the ventral aorta.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Ventral Aorta:
Lying in the subendostylar coelom, below the pharynx, is a contractile ventral aorta which pumps blood forwards by peristaltic contractions. At the anterior end the ventral aorta passes into two external carotid arteries. From the ventral aorta paired afferent branchial arteries arise and pass upwards in the pharyngeal wall on both sides.
The afferent branchial arteries at their commencement have contractile dilations called bulbilli which also pump blood, then they pass through the primary gill bars as three branches and through the synapticula they give two branches to each secondary gill-bar.
They form vascular plexuses which supply nephridia. Blood is collected from the gill-bars and nephridia by aortic arches or paired efferent branchial vessels. In the afferent and efferent vessels the blood is exposed to a respiratory water current, but there is no proof of its oxygenation since there is no respiratory pigment in the blood.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The efferent branchial vessels of each side open into a lateral dorsal aorta lying on the side of the epipharyngeal groove. The right lateral dorsal aorta is more dilated than the left one; each is continued in front into the rostrum as an internal carotid artery to supply the blood to oral hood region.
Dorsal Aorta:
The two lateral dorsal aortae unite behind the pharynx to form a median dorsal aorta lying between the notochord and intestine. The dorsal aorta gives out many small, paired parietal arteries to the body wall and intestinal arteries to the intestine where they form plexuses in lymph spaces, then it is continued backwards as a caudal artery into the tail. Blood flows backwards in the dorsal aorta.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
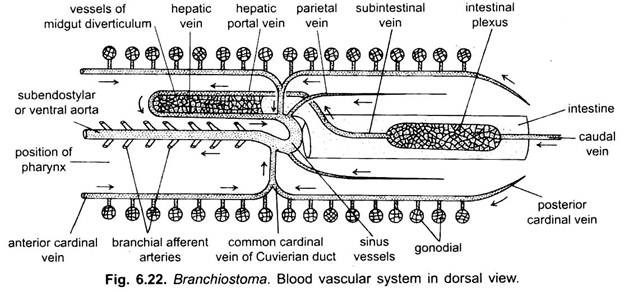
Subintestinal Vein:
From the lymph spaces of the intestine blood is collected into a median longitudinal a subintestinal vein. For a greater part of its length the subintestinal is not a single vein but a plexus of small vessels, it runs below the intestine, and blood flows forwards in it; The blood from the tail is collected by a caudal vein which in the intestinal region joins the plexuses of the subintestinal vein.
Hepatic Portal System:
The subintestinal vein in the anterior part of the midgut form a short but wide hepatic portal vein which runs along the ventral border of the midgut diverticulum and ramifies in its wall, thus, forming a system which is not strictly comparable with, but which foreshadows the hepatic portal system of vertebrates. Small blood vessels from the midgut diverticulum unite to form a short hepatic vein running along the dorsal border of the midgut diverticulum. The hepatic vein enters a sac-like sinus venosus from which arises the ventral aorta.
Parietal Veins:
A pair of parietal veins lying on either side of the gut receives blood from the dorsal body wall. They run dorsal to the intestine for a short distance and then run ventrally to open into the sinus venosus.
Cardinal Veins:
Running in the body wall at the level of gonads on each side are an anterior cardinal and a posterior cardinal veins which receive blood through small segmental veins coming from the body wall, myotomes and gonads. The anterior and posterior cardinal veins of each side unite just behind pharynx to form a ductus Cuvieri or common cardinal vein. The two ductus Cuvieri pass inwards through the atrium to join the sinus venosus.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
A renal portal and a true hepatic portal system are absent because of the absence of kidneys and a true liver, yet the circulatory system is of the pattern found in vertebrates.
Course of Blood Circulation:
Blood flows anteriorly in the caudal, sub intestinal, parietals, posterior cardinals and ventral aorta. Whereas in the laterals and median dorsal aorta and anterior cardinals, it flows backwards.
Lymphatic System:
Lymphatic spaces or sinuses are present in the cavities containing fin rays of the dorsal and ventral fins, and paired canals in the metapleural folds. These spaces are filled with colourless blood having no leucocytes. The measure amount of O2 required by Branchiostoma may be taken into the blood through these superficial areas.