The circulatory system of Channa Punctatus comprises of:
(i) The circulatory fluid—the blood,
(ii) The pumping organ—the heart,
(iii) The arteries and
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(iv) The veins.
(i) Blood:
Blood is a pale-coloured fluid. It contains elliptical, nucleated erythrocytes and amoeboid leucocytes suspended in the plasma.
(ii) Heart:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Heart is located ventral to the oesophagus in the pericardial section of the coelom. It is enclosed within a thin pericardium. It is constructed by two types of chambers:
(a) Receiving chambers:
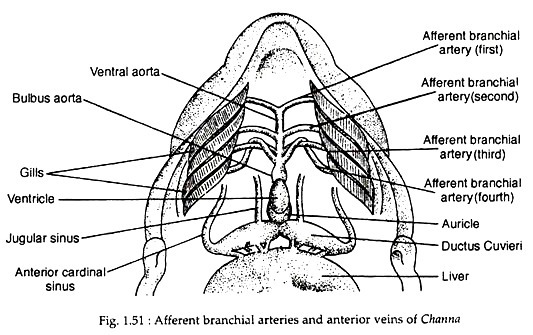
The sinus venosus and the auricle constitute the receiving parts of the heart. The sinus venosus is a dorsally placed thin-walled sac. It receives deoxygenated blood by two caval veins or ductus Cuveiri. The auricle is a single thin walled chamber and is situated ventral to the sinus venosus. The sinus venosus opens to the auricle by a Sino auricular aperture which is guarded by valve.
The auricle opens into the ventricle by auriculoventricular aperture. This aperture is guarded by valves. Through both these aforesaid apertures the blood flows in the direction from sinus venosus to auricle and from auricle to the ventricle, respectively. The valves guarding the apertures prevent the change of direction or back-flow of blood and thus maintain a unidirectional flow of blood through the different parts of the heart.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(b) Forwarding chamber:
The forwarding chamber of the heart is exclusively the thick-walled conical ventricle. It is placed ventral to the auricle. There is no conus arteriosus. This part of the heart is represented by a pair of valves guarding the entrance of the bulbus aorta. The bulbus aorta is a dilated part at the base of the ventral aorta and is not to be-regarded as the component part of the heart.
(iii) Arterial System:
The arterial system of the lata consists of two categories of arteries depending on the type of blood the vessels carry. The afferent branchial arteries carry the deoxygenated blood from the heart to the gills and the efferent branchial arteries collect oxygenated blood from the gills and convey it to the different parts of the body.
Afferent branchial system:
The deoxygenated blood from the ventricular cavity is conveyed through a stout median ventral aorta to the gills for aeration by four pairs of afferent branchial arteries (Fig. 1.51). All the four pairs of the afferent branchial arteries have independent origin from the ventral aorta.
The first and second pairs of the afferent branchial arteries are simple straight arteries leading from the ventral aorta to the corresponding pairs of gills. The third and fourth afferent branchial arteries arise from one point of ventral aorta and cross each other forming a loop after their origin (Fig. 1.51).
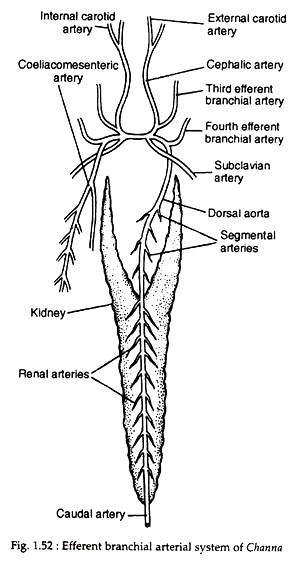
Efferent branchial system:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The first and second pairs of efferent branchial arteries are lacking (Fig. 1.52). The third efferent branchial artery on each side receives oxygenated blood from the third gill of that side and gives off a cephalic artery or common carotid artery. This artery runs forward and bifurcates into an external carotid artery and an internal carotid artery.
A transverse artery acts as a connecting bridge between the third and fourth efferent branchial arteries of the two sides. The left fourth efferent branchial artery gives origin to the dorsal aorta. The coeliacomesenteric artery originates from the point of union of the transverse artery and the right fourth efferent branchial artery.
Two subclavian arteries arise independently on the two sides and each divides into two arteries — the pectoral artery supplying the pectoral fin and a pelvic artery to the pelvic fin. The dorsal aorta occupies a mid-dorsal position and runs posteriorly up to the tail as caudal artery. Along its course it gives off paired segmental arteries, gonadal arteries and renal arteries.
The oxygenated blood from the first two pairs of gills is possibly drained into the supra-branchial cavity directly through some sort of capillary networks. These capillary networks together with that of the supra-branchial cavity unite to form an artery which joins with the cephalic arteries.
(iv) Venous System:
The venous system of Channa Punctatus consists of the systemic veins and the portal veins. These veins directly or indirectly convey the deoxygenated blood from the different parts of the body to the heart.
(a) Systemic venous system:
The blood is carried to the sinus venosus by right and left ductus Cuvieri. Each ductus Cuvieri is formed by three principal veins: an anterior cardinal sinus, a jugular sinus and a posterior cardinal sinus. The anterior cardinal sinus brings blood from the anterior part of the body and the posterior cardinal sinus brings blood from the posterior part of the body. Both the posterior cardinal veins receive segmental veins, renal veins, genital veins, etc.
In addition to the above-mentioned three principal veins, the pectoral and pelvic veins form the pectoral and pelvic fins, respectively, and the slender hepatic vein opens into the ductus Cuvieri. The blood from the tail region is conveyed by a caudal vein which just after entering into the trunk bifurcates into two branches.
The right posterior cardinal sinus passes through the substance of the right kidney and opens into the right ductus Cuvieri. The left posterior cardinal vein originates from the capillaries of the renal portal vein.
(b) Portal veins:
The portal venous system is composed of a special vein which originates in capillaries and end in capillaries and secondly the blood from these veins before going to the heart passes through some intermediate organs. When the intermediate organ is the kidney, such a system constitutes the renal portal system and when the organ is liver, the system is called the hepatic portal system.
(i) Renal portal system:
The left branch of the caudal vein after entering into the left kidney breaks up into capillaries and forms the renal portal vein. These capillaries reunite and form the left posterior cardinal vein.
(ii) Hepatic portal system:
The capillaries from the alimentary canal and its associated structures unite to form a hepatic portal vein which enters into the substance of liver and breaks up into the capillaries. The capillaries reunite to form the hepatic vein which opens to the ductus Cuvieri.