In this article we will discuss about:- 1. Habit and Habitat of Channa Punctatus 2. Geographical Distribution of Channa Punctatus 3. External Structures 4. Digestive System 5. Excretory System 6. Reproductive System.
Contents:
- Habit and Habitat of Channa Punctatus
- Geographical Distribution of Channa Punctatus
- External Structures of Channa Punctatus
- Digestive System of Channa Punctatus
- Excretory System of Channa Punctatus
- Reproductive System of Channa Punctatus
1. Habit and Habitat of Channa Punctatus:
The lata fish inhabits fresh-water ponds and ditches. It is usually carnivorous and eats other small fishes and small aquatic animals. Lata fish is notable for migration overland from one pond to another during rains. The ability to breathe in air by its accessory respiratory organ helps the fish to thrive well out of water for a considerable period of time.
2. Geographical Distribution of Channa Punctatus:
Channa Punctatus is found throughout the plains of India, Pakistan and Bangladesh.
3. External Structures of Channa Punctatus:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
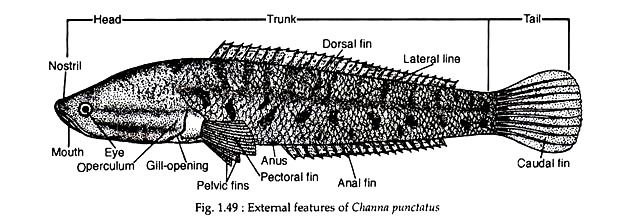
The body of Channa Punctatus is elongated (Fig. 1.49) and covered with ctenoid scales. It has been recorded that cycloid scales are also present. Both the scales are systematically arranged cycloid and prectenoid. The body is divided into head, trunk and tail regions. The head is depressed and covered by large plate-like scales resembling the ‘head shields’ of snakes.
The eyes are placed on the lateral sides of the head. The dorsal fin is single. The anal fin extends from the posterior end of the anus. Both the dorsal and anal fins are undivided and are supported by spinous bony fin-rays. The caudal fin is unilobed.
4. Digestive System of Channa Punctatus:
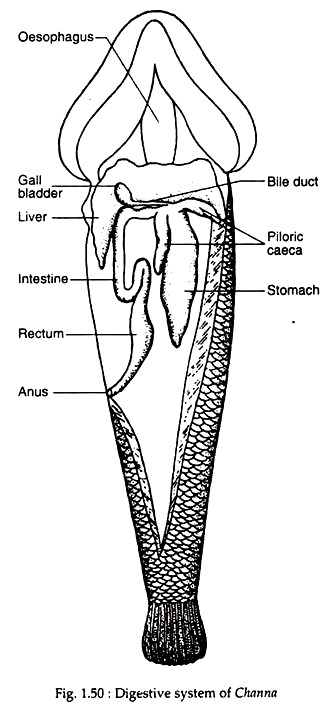
Mouth is bounded by upper and lower jaws. Jaws are provided with sharp conical teeth. The buccal cavity is spacious and leads into a short tubular oesophagus. Stomach is an elongated sac-like structure. The most important feature to note in the digestive system of lata is the presence of only two pyloric caeca (Fig. 1.50).
These caeca open at the junction of the intestine and the pyloric end of the stomach. The intestine is a coiled tube with its distal part dilated as rectum. Anus is located on the ventral surface and in front of the anal fin.
The liver is a distinct bilobed glandular structure. Bile produced in the liver is stored in the gall-bladder situated on the ventral side of the right lobe of liver. The bile duct opens into the intestine just near the point of origin of the pyloric caeca.
5. Excretory System of Channa Punctatus:
The excretory organ of Channa Punctatus comprises of two elongated kidneys located ventral to the vertebral column and extending the whole of coelom. The kidneys are of mesonephric type. The two kidneys are fused partially at their posterior ends. Each kidney is composed of numerous uriniferous tubules.
On the ventral surface many minute apertures called nephrostomes are present. These apertures communicate with the uriniferous tubules. The uriniferous tubules open to a tube called ureter which emerges from the posterior part of the kidney.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Two ureters from the two kidneys unite at the posterior end to form a common ureter which communicates with the urinary bladder. The bladder in turn opens to vent through a narrow duct. The urinary bladder in this fish is a mesodermal derivative and as such is not homologous to the endodermal bladder of higher vertebrates.
6. Reproductive System of Channa Punctatus:
Sexes are separate. Gonads exhibit seasonal variation and attain maximum size during breeding season.
Male reproductive system:
The testes are two in number and are elongated structures. Each testis is composed of seminiferous tubules and gives out a vas deferens which opens to the lateral side of the vent. There are two genital openings.
Female reproductive system:
The ovaries are much longer than the testes and contain numerous eggs. Matured eggs are conveyed through the oviducts and are discharged to exterior by reproductive openings. There are two genital openings located at the lateral sides of the vent.