In this article we will discuss about the Phylum Platyhelminthes:- 1. Classification of Phylum Platyhelminthes 2. Diagnostic Features of Phylum Platyhelminthes 3. Scheme of Classification 4. Systematic Resume.
Classification of Phylum Platyhelminthes:
In the evolutionary process, the evolving of mesoderm, a third layer between ectoderm and endoderm has further resulted in structural complexities, coupled with increased in size. Animals built on this three layered foundation have been designated as triploblastic. Platyhelminthes is considered to be one of the primitive triploblastic groups.
Platyhelminthes or flatworms are a diverse group comprising of 25000 living species that show evolutionary achievements over the diplo-blasts in having a structural body plan that is based on bilateral symmetry and in having definite organs or system of organs.
They, however, lack coelom (the space between the various organs being filled with a special connective tissue called parenchyma), the body being compact (acoelomate) and the absence of blood vascular system.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Etymology:
Greek: platy, flat; helminthes, worms.
Diagnostic Features of Phylum Platyhelminthes:
i. Body bilaterally symmetrical and dorsoventrally flattened.
ii. They are triploblastic acoelomate, animals, having organ systems that occur in the middle layer.
iii. Mainly soft-bodied but with protective mucous secretions and a few species with internal spicules.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
iv. Digestive system has a single opening or mouth, that leads to a well-developed gastro-vascular cavity. Anus absent.
v. Circulatory and respiratory organs are absent. Gaseous exchange by diffusion.
vi. Protonephridial ‘excretory’ organ and its function is probably largely osmoregulatory than excretory. True excretory products leave the body mainly by diffusion.
vii. Nervous system consists of nerve nets which are usually concentrated in longitudinal fibres.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
viii. Typically they bear anterior eyespots, chemoreceptive organs and a rudimentary brain.
ix. Generally hermaphrodite.
x. Sperm is filiform and thread like. Cleavage is spiral.
xi. In free-living forms development is generally direct (in some there is a free- swimming Muller’s or Gotte’s larva). Development in some parasitic forms is very elaborate, involving several larval stages.
xii. Occurs in all major habitats, aquatic and terrestrial, including the tissues of other animals.
Scheme of Classification of Phylum Platyhelminthes:
Linnaeus (1735) first included platyhelminthes with other worms in the phylum Vermes. Lamarck (1816) separated them from other worms and Cuvier (1813) included them within Zoophyte or Radiata. The name platyhelminthes was first coined by Minot in 1876. They were later classified differently by different authors.
The phylum Platyhelminthes is divided into four classes. Three are entirely parasitic and include Trematoda, Monogenea and Cestoidea (tapeworms). The fourth class, Turbelaria, is free-living and from this group arose the ancestors of the three parasitic classes.
In this text the classificatory scheme followed is that of Ruppert and Barnes, 1994 (6th edn.).
Systematic Resume of Phylum Platyhelminthes:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Class Turbellaria:
i. Turbellarians are mainly free-living and aquatic (majority marine, few fresh water), but there are some terrestrial species also confined to humid areas. Aquatic forms are benthic.
ii. Body size ranges from a few millimeters to 50 centimeters.
iii. An acoelomate grade of body construction present with a low level of cephalization.
iv. Most turbellarians move by cilia (lining the epidermis), which provide the propulsive force; larger forms (poly- clads) are markedly flattened and move by combine ciliary motion with muscular undulations.
v. Mucus produced from the gland cells, lubricates and protects the body surface, provides leverage for the cilia and is used in the capture of food by entangling the prey.
vi. The mouth, which is present on the ventral surface, is located at the end of an eversible pharynx and leads into a sac-like, lobed or much branched intestine.
vii. Digestion is initially extracellular and then intracellular. Most turbellarians are predators and scavengers while a few are herbivores, commensals or parasites.
viii. Excretion by protonephridia.
ix. Several pairs of longitudinal nerve cord are radially arranged and associated with peripheral nerve nets. Numerous pigment cup, ocelli and statocysts are the principal sensory organs.
x. Hermaphrodite, with internal fertilization. Cleavage is spiral and development is direct in most species. Many turbellarians also reproduce asexually by means of budding or transverse fission and show high power of regeneration.
Examples:
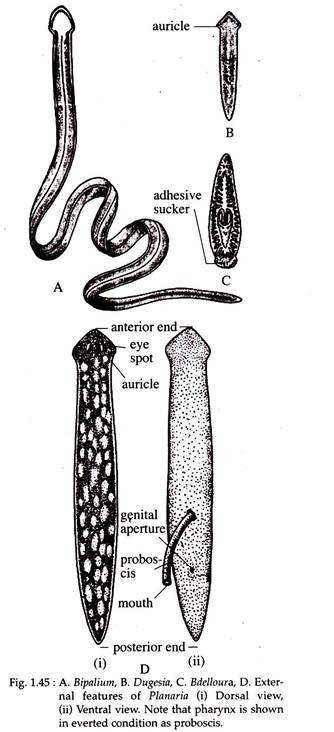
Ectocotyla (commensal on hermit crab), Planeria (fresh water flat worm) (Fig. 1.45D), Anaperus (marine flat worm), Gyratrix (marine interstitial species), Stenostomum (fresh water species), Bipalium (land planarian) (Fig. 1.45A), Bdelloura (horse-shoe crab, commensal) (Fig. 1.45C), Dugesia (fresh water) (Fig. 1.45B).
Class Trematoda:
i. All are parasites, occurring especially in vertebrates.
ii. Body cylindrical or leaf shaped.
iii. Rhabdites or cilia are absent.
iv. Body is covered by cuticle, which provides protection against hosts enzyme- action and defense mechanism.
v. Suckers and acetabulum present for attachment.
vi. Mouth is anteriorly situated.
vii. A well-developed gut is present.
viii. In most cases the testes are two but always one ovary is present. Reproduction is always sexual.
Subclass Digenea:
i. Endoparasites in all classes of vertebrates and are commonly known as flukes.
ii. Adult digeneans are about 0.2 mm to 6.0 cm in length.
iii. Dorsoventrally flattened body, some are thick and fleshy, whereas others are long and thread-like.
iv. Presence of an oral sucker surrounding the mouth and many have a mid-ventral or posterio-ventral sucker.
v. A gut is present and digestion is primarily extracellular.
vi. Body covered by non-ciliated, protective tegument.
vii. Digeneans are facultative anaerobes.
viii. Excretion by protonephridia.
ix. Nervous system (similar to turbellarians) comprises of a pair of anterior cerebral ganglia from which longitudinal nerve cords extend posteriorly.
x. Hermaphrodite, with the male part comprising of two testes and the female part of a single ovary. Cross fertilization is the general rule.
xi. The digenean life cycle is indirect and involves two to four different hosts and a number of developmental stages, comprising of three or four types of larvae (miracidium, sporocyst, redia, cercaria).
Examples:
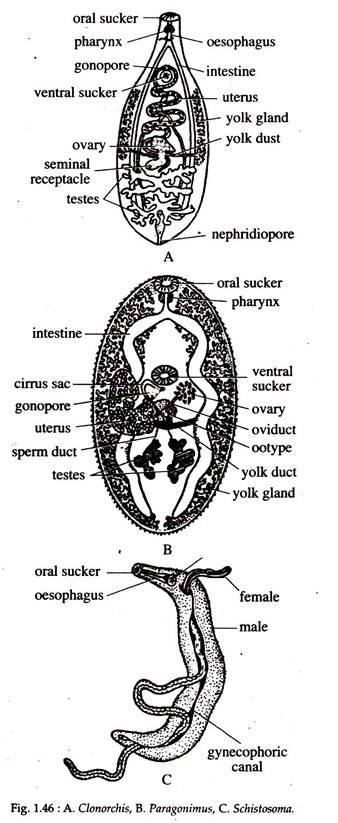
Schistosoma (Fig. 1.46C), Fasciola (Fig. 1.50), Clonorchis (Fig. 1.46A), Opistorchis, Paragonimus (Fig. 1.46B).
Subclass Aspidogastrea:
i. Aspidogastreans are mostly endoparasites in the gut of fishes and reptiles and in the pericardial and renal cavities of bivalve molluscs.
ii. Adhesive organ comprises of either a single sucker covering the entire ventral surface or a longitudinal row of suckers.
iii. The digestive tract comprises of a single intestinal caecum.
iv. Male reproductive system includes only one testis.
v. Life cycle involves one or two hosts.
Examples:
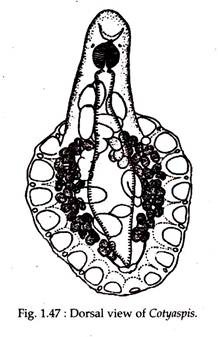
Cotyaspis (Fig. 1.47), Aspido- gaster.
Class Monogenea:
i. Monogeneans are mostly ectoparasites of aquatic vertebrates, particularly fishes, but amphibians, reptiles and cephalopod molluscs are also hosts.
ii. Body dorsoventrally flattened and have a large, posterior attachment organ, the haptor, which bears hooks and suckers.
iii. Anterior end has also adhesive glands.
iv. A gut is present -but mouth lacks a sucker. The pharynx secretes a protease that digests the host’s skin.
v. They respire aerobically, being ectoparasites.
vi. Monogeneans have inconspicuous proto- nephridia for excretion.
vii. All members are hermaphrodite.
viii. Life cycle simple and having no intermediate host.
ix. One egg by way of a ciliate larva (Oncomiracidium) gives rise to only one adult worm and hence the name monogenea meaning “one generation”.
Examples:
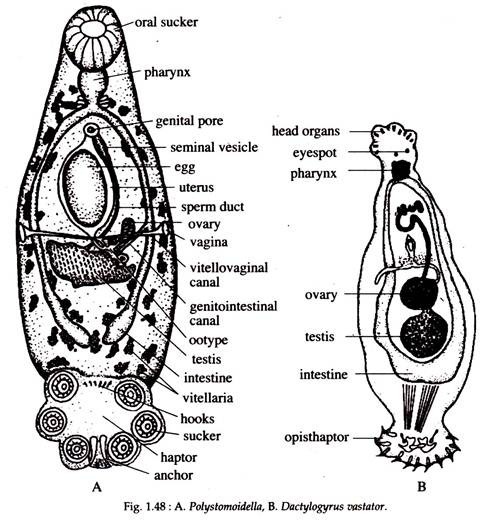
Poly stoma (bladder of frogs), Polystomoidella (Urinary bladder of turtles) (Fig. 1.48A), Dactylogyrus (gills of freshwater fishes) (Fig. 1.48B).
Class Cestoidea:
i. Endoparasitic helminth, whose body is covered by a syncytial tegument.
ii. Cestoideans have special tegumental modifications associated with nutrient uptake as they lack a mouth and digestive tract.
iii. Organs of attachment in the form of hooks and suckers are present.
iv. Absence of sense organs.
v. Each segment excepting the head and neck is provided with one or two sets of complete sex organs.
vi. Hermaphrodite. Life cycle is complicated and involves a larval stage.
Subclass Eucestoda:
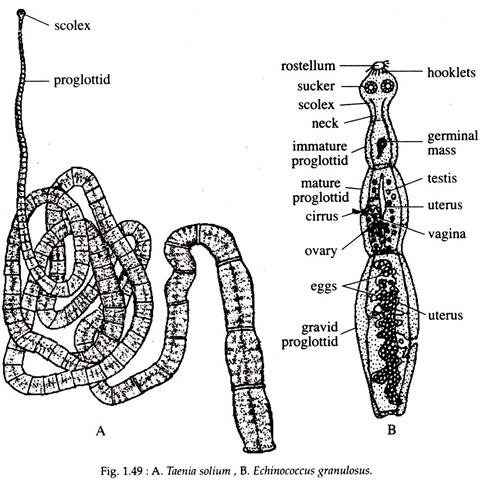
i. Body long, segmented, ribbon-like and is commonly known as tapeworm.
ii. Body consists of three regions, viz., scolex, neck and strobila.
iii. Scolex, the anterior head region, is generally a four-sided knob provided with suckers or hooks for attachment to the host gut.
iv. The strobila consists of linearly arranged segment-like sections, called proglottids.
v. Cross-fertilization is the common rule, but self-fertilization between two proglottids or within the same proglottid may occur.
vi. In eucestodeans, life cycle involves one, two or sometimes more intermediate hosts, which are usually arthropods and vertebrates.
vii. Life cycle is indirect and involves a ciliated, free-swimming larva called oncosphere (coracidium), which bears six small hooks.
Examples:
Taenia solium (pork tape worm) (Fig. 1.49A), Taenia saginatus (beef tape worm), Echinococcus granulosus (hook worm) (Fig. 1.49B),’ Diphyllobothrium (parasite in the gut of many fish-eating- carnivores), Echinobothrium (parasite in elasmobranch fishes), Proteocephalus (parasite in the intestine of fish, amphibia and reptile).
Subclass Cestodaria:
i. Body small and undivided.
ii. Absence of scolex.
iii. Presence of sucker on the anterior end of the body.
iv. Proglottid absent.
v. One set of reproductive structure is present.
vi. Larva is with ten hooks.
Examples:
Amphibian (parasite in sturgeon fish), Gyrocotyle (parasite in chimaeroid fish).