The following three points highlight the classification of aschelminthes: 1. Enterobius Classification 2. Ascaris Classification 3. Ancylostoma Classification.
Type # 1. Enterobius Classification:
Phylum: Aschelminthes Pseudo coelomate, vermiform; un-segmented or superficially segmented clothed with cuticle; straight or curved digestive tube.
Class: Nemotoda Body un-segmented; cilia absent; alimentary canal straight or curved.
Order: Oxyuroidea Parasitic on vertebrates; three or six lips, buccal capsule small; pharynx with a posterior bulb; male with one or two spicules.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Genus: Enterobius
Species: Vermicularis
Comments:
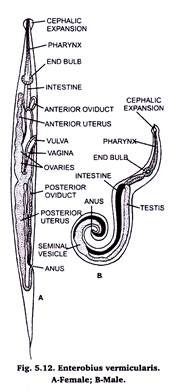
1. Enterobius vermicularis (Fig. 5.12) is commonly known aspin-worm orseat-worm or thread-worm.
2. It has three small lips and a pair of cephalic expansions at the anterior end.
3. Female is 10 mm long with a long pointed tail.
4. Male is 3-5 mm long with blunt, curved tail with a bursa-like expansion and a single spicule. Mals are few and rare.
5. Fertilized females make nighty trips to the anus to lay eggs or they may creep out of the anus and lay eggs.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
6. Eggs are well advanced when laid, each contains a tadpole-like juvenile.
7. Persons reinfect themselves by scratching with hands from where eggs may get into the mouth. Eggs may infect the entire family through clothes, furniture, air and dust in the room.
8. Eggs hatch in small intestine, the juveniles descend slowly, moult 4 times and become adults.
9. Enterobius causes pinworm disease or enterobiasis, their movements cause intense itching of the anus, inflammation of muscous membrane of colon and appendix and often insomnia and lack of appetite.
10. Enteric-coated capsules of gentian violet of one grain given by for days removes most of the worms.
Habit and habitat:
Enterobius vermicularis is cosmopolitan, but more common in Europe and America, in some communities 40-100% of the population may be infected. It is a parasite in the human caecum, colon and appendix.
Type # 2. Ascaris Classification:
Phylum: Aschelminthes Pseudo coelomate, vermiform; un-segmented or superficially segmented clothed with cuticle; straight or curved digestive tract.
Class: Nemotoda Body un-segmented; cilia absent; alimentary canal straight.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Order: Ascaroidea Parasitic in the intestine of vertebrates; three prominent lips; pharynx without a posterior bulb; tail in female straight and blunt tail in male with two spicules.
Genus: Ascaris
Species: Lumbricoides
Comments:
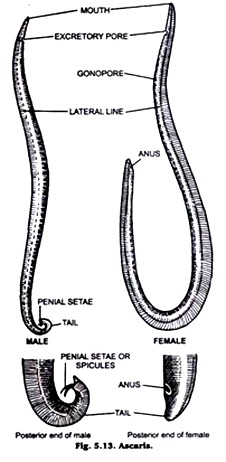
1. Ascaris lumbricoides (Fig. 5.13) is commonly known as roundworm.
2. Body is elongated, cylindrical, pointed at both ends.
3. Surface of the body is marked with four longitudinal lines, these are known as mid-dorsal, mid-ventral and two lateral lines.
4. Mouth provided with a median dorsal and a pair of symmetrical sub-median ventral lips.
5. Excretory pore is small and lies on the ventral side about 2 mm away from the anterior end.
6. Sexes are separate and sexual dimorphism is well marked.
7. Male is about 15 to 31 cm in length with the posterior end curved ventrally.
8. Male is provided with a pair of curved spicules known aspenial setae on its posterior end.
9. Female is large reaching a length of 20 to 35 cm with the posterior end straight and blunt.
10. Female gential aperture lies about one-third of the length of the body from the anterior end.
11. The disease caused by this parasite is called ascarisis.
12. Ascariasis is more common in children than in adults.
13. Its infection occurs by eating raw and uncooked vegetables infected with its eggs.
14. Its life history is completed in one host only (man), t. e.,monogenetic.
Habit and habitat:
Ascaris lumbricoides is a common endoparasite in the small intestine of in all parts of the world.
Type # 3. Ancylostoma Classification:
Phylum:Aschelminthes Pseudo coelomate, vermiform; un-segmented or superficially segmented clothed with cuticle; straight or curved digestive tube.
Class: Nemotoda Body un-segmented; cilia absent; alimentary canal straight.
Order: Strongyloidea: Parasitic in the digestive tract of vertebrates; mouth without lips but with leaf crowns; pharynx without bulbs; females with ovejecters; males with a copulatory bursa.
Genus: Ancylastoma
Species: Ducodenale
Comments:
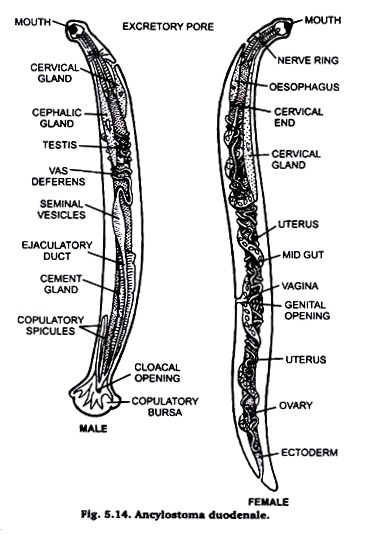
1. Ascylostoma (Fig. 5.14) is commonly hookworm.
2. Mature worm is cylindrical in shape, narrow anteriorly and white or ivory grey in colour.
3. Males measure 8-11 mm in length and females measure 10-13 mm in length.
4. Buccal cavity is oval and the buccal capsule is made of articulated grooved portion.
5. Excretory pore mid- ventral in position just behind the nerve ring.
6. Male is provided with a campanulate bursa which is broader than long and supported by fleshy rays.
7. Vulva of the female is behind the middle part of the body and the tail is tipped by a minute pine.
8. Fertilization is internal and occurs in the intestine of host. Fertilized eggs passed out with the faeces and after some time develop into infective stage.
9. Infection takes place by penetration of the skin of host by the infective larval stage.
10. Ancylostoma duodenale causes severe injury to the intestine and other parts of the host collectively referred to asancylostomiasis.
Habit and habitat:
Ancylostoma duodenale is found as an endoparasite in the intestine of man. It is endemic in Western Europe, tropical and subtropical Asia. Africa and various Pacific Islands and South America.