In this article we will discuss about the external structure of toad. This will also help you to draw the structure and diagram of toad.
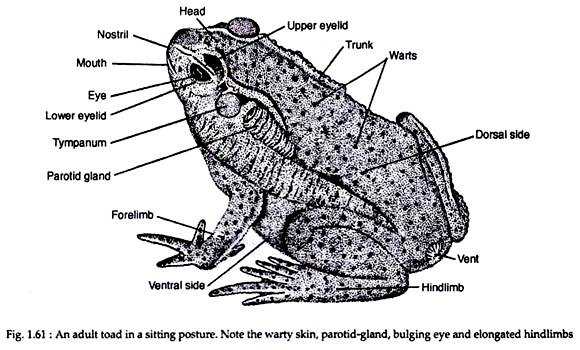
Toad has a short bilaterally symmetrical body (Fig. 1.61). There is no exoskeleton over the skin, i.e., the skin is naked skin is rough in texture. The dorsal side of the body is blackish-gray while the ventral side is yellowish grey. Toad can change the colour of the body to match with the hues of its surroundings.
Ordinarily, its body colour is same as that of the earth. The body is divisible into head and trunk. Distinct neck is absent. A postanal tail is absent in adult stage. The tail is present and well-developed in the larval condition. The head is semicircular in outline. It is broad, depressed and has a blunt snout.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Mouth is a wide opening located at the terminal end of the head. At the anterior dorsal side of the head there is a pair of rounded openings known as nostrils or external nares. The eyes are very large and prominent. Each eye is provided with a thick upper eyelid and an ill-developed lower eyelid.
A transparent nictitating membrane (or third eyelid) is present and it is stretched to cover the eye ball. Behind each eye, a circular area known as eardrum (or tympanum) is present. Just behind each tympanum there is an elongated elevation called parotid gland. These paired glands secrete a whitish, pungent, sticky poisonous juice.
These glands act as the organs of offense and defence. The skin on the floor of the buccal cavity becomes inflated to form vocal sac in males. The trunk is broad, short and flattened. Numerous small bumps known as warts are present on the dorsal side of the body. The cloacal aperture or vent is located on the dorsal side of the posterior end of the body between the two hind limbs.
There are two pairs of limbs. These are of unequal size. The forelimbs are smaller than the hind limbs. Each forelimb consists of brachium (upper arm), and ante-brachium (forearm), a wrist and a manus (hand). The hand is followed by four digits. In male individual, a cushion-like thumb pad (or nuptial pad) develops during breeding season at the basal part of inner finger. These pads fascilitate the males grip during copulation.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The hind limbs are strongly built and are much longer than the forelimbs. These two limbs are modified for jumping and swimming. Each hind limb is composed of a proximal sector called femur (thigh) which is followed by crus (shank). Distal to the shank lies the pes (foot). The foot consists of five elongated slender digits. The digits are united by webs which help in swimming.
Skin:
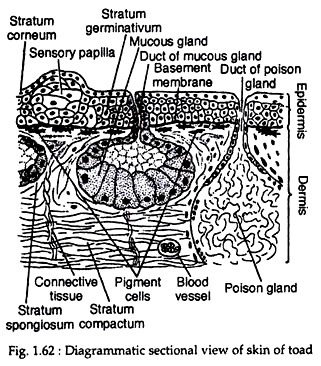
The skin is composed of an outer epidermis and an inner dermis (Fig. 1.62). These two layers are separated by a basement membrane and a fibrous layer containing the chromatophores or pigment cells. The epidermis is a compound structure and is made up of several layers.
The outermost layer is called stratum corneum. It is a thin, scaly and cornified layer. This layer is dead and is shed periodically. This phenomenon of periodic shedding of the stratum corneum is called ecdysis (or moulting). The innermost layer of the epidermis is composed of columnar cells with prominent nuclei.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
This layer is called stratum germinativum (or Malpighian layer) which lies on the basement membrane. The cells lying between the stratum germinativum and stratum corneum constitute the transitional layer. These cells form several layers and decrease in size from below upwards.
The dermis is thicker than the epidermis and is divisible into two layers. The outer layer accommodating most of the glands is called stratum spongiosum. This is composed of loose network of connective tissue matrix with blood vessels and lymphatic spaces. The superficial part of this layer contains the pigment cells.
The innermost layer is called stratum compactum, which is composed of dense connective tissue, smooth muscle fibers, nerves and blood vessels. Beneath the stratum compactum lies a loose subcutaneous connective tissue layer containing fatty tissue.
The skin of toad is marked by the presence of numerous bumps (or warts) all over the dorsal body surface. These warts may be either due to underlying poison glands or sensory papillae. There are two types of skin glands in toad. These are mucus glands secreting mucus and poison glands producing poison. The mucus glands are smaller than the poison glands. The poison glands are composed of granular secretory cells.
The skin glands usually lie in the stratum spongiosum of the dermis, but the poison glands may be more deeply located. These glands are unsheathed by connective and muscular tissues, which help in squeezing the secretory products.
The products of the gland come out through duct to the outside. The skin of toad is always remains moist and slimy. Besides its protective function, the skin of toad serves as an additional respiratory organ. During hibernation, toad respires entirely by the skin.
Colouration:
The colour of toad depends upon the presence of pigment cells or chromatophores in the dermis. Some chromatophores also invade the epidermis. Depending on the types of contained pigment granules, the chromatophores may be melanophores (containing black pigment), guanophores (containing colourless crystals of guanine) and lipophores (containing yellow pigment).
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The melanophores are situated in the deepest layer; the guanophores are intermediate in position while the lipophores are present in the upper layer.
The melanophores are responsible for the production of blackish colour and the lipophores cause yellowish effect. The guanine crystals in the guanophores produce diffraction effect. The colour change in toad is rather a slow process and is controlled under the action of melanophore stimulating hormone (MSH) of the pituitary gland. The colour change in toad is not under nervous control.