In this article we will discuss about the digestive structure of toad.
The digestive system consists of alimentary canal and its associated digestive glands. The alimentary canal is a long tube which starts from the mouth and ends in the cloaca. The alimentary canal is made up of four layers. The outermost layer is thin and called serous coat. Next to the serous coat lies the muscular layer which is composed of outer longitudinal muscles and the inner circular muscles.
The innermost layer lining the lumen is the mucous coat. The mucous layer is composed of epithelial cells and glands at certain regions. The region between the muscular coat and the mucous coat is filled up with connective tissue matrix with blood and lymphatic vessels. This layer is known as sub mucous coat.
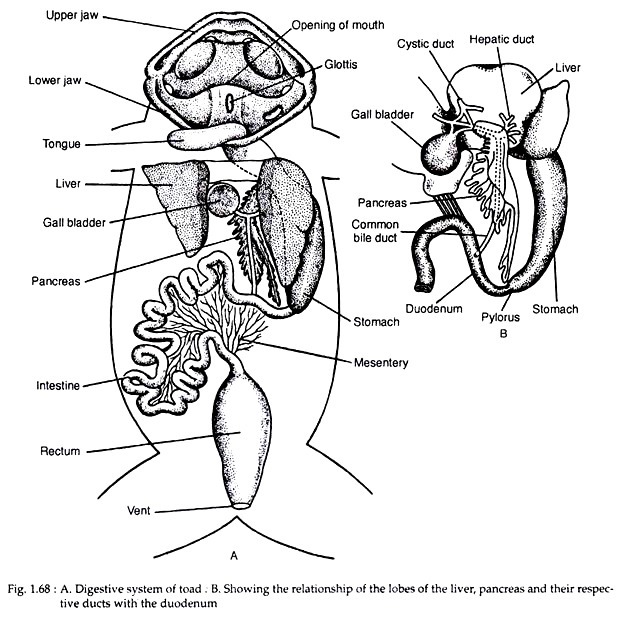
The mouth is a wide aperture and is bounded by upper and lower jaws. Both the jaws are toothless. The mouth leads into a spacious buccal cavity. The roof of the buccal cavity contains a pair of internal nostrils, impressions of the eyeballs, a pair of eustachian apertures.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The floor of the buccal cavity bears a large fleshy tongue which is attached to the hyoid arch. The tongue is fixed anteriorly but free behind. The tongue is kept sticky by the secretion of inter-maxillary glands. It can quickly be protruded to capture insects. Behind the tongue there is a longitudinal slit called glottis which leads into the laryngotracheal chamber.
There are mucous glands in the buccal cavity which do not produce any enzyme. There is a system of cilia in the buccal cavity which possibly keep the oral fluid in circulation. The buccal cavity narrows towards the pharynx which leads into a wide tube known as oesophagus or gullet.
The oesophagus opens into the stomach. The stomach is a thick-walled spacious sac and is slightly curved (Fig. 1.68A). The broad anterior part of the stomach is known as cardiac end and the other end is called pyloric end. The pyloric part of the stomach opens into intestine. This opening is guarded by circular sphincter muscle called pyloric valve which regulates the exit of food from the stomach.
The mucous coat of the stomach opens into intestine. This opening is guarded by circular spinster muscle called pyloric valve which regulates the exit of food from the stomach. The mucous coat of the stomach contains tubular gastric glands which secrete digestive juices and unicellular parietal glands (or oxyntic cells) which secrete hydrochloric acid.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
In addition to the longitudinal and circular muscle layers in the muscular coat, oblique muscles are present in the stomach. The part of the intestine next to stomach is known as small intestine which is again divided into an anterior short duodenum and posteriorly into an ileum.
The duodenum receives duct from liver and pancreas. The ileum is extensively coiled and is held in position by mesentery. The mucous coat of the ileum gives off numerous fingerlike elevations known as villi which increase the inner surface areas. In addition, it contains intestinal glands which secrete intestinal juices.
The portion of alimentary canal next to ileum is usually called large intestine which is divided into rectum and cloaca. The cloaca is a common chamber where urine, gametes and faecal matters are temporarily stored. The cloaca opens to the exterior through the vent (or cloacal aperture).
Besides gastric and intestinal glands, the liver and the pancreas are the important digestive glands. The liver is the largest gland and consists of two main lobes — left and right. The lobes are connected with one another by a bridge.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The left lobe of the liver is the larger one and is subdivided into two lobes. The secretory as well as excretory products of the liver are called bile. The bile comes out by hepatic ducts and is stored in the gall-bladder (Fig. 1.68B).
The cystic duct from the gall-bladder and the hepatic duct from the liver unite to form the common bile duct. This common bile duct passes through pancreas and receives numerous minute pancreatic ducts. The common bile duct is usually called hepatopancreatic duct which ultimately opens into the duodenum to pour the hepatopancreatic juices into the duodenal cavity.
The pancreas is an irregular and yellowish gland. It is both an exocrine as well as endocrine gland. The exocrine part secretes the pancreatic juice. The endocrine part, islets of Langerhans, produces hormones.
Physiology of digestion:
Toad is a carnivorous animal which feeds on small animals, preferably the insects. Its food consists primarily of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, mineral salt and water. The vitamins, mineral salts and water are absorbed as such but the carbohydrates, proteins and fats are complex organic compounds which cannot be absorbed unless these are broken down into simpler forms.
Digestion is effected by the digestive juices. These juices contain three groups of enzymes amylolytic or diastatic enzymes, such as the amylase of the pancreatic juice, lipolytic enzyme, the lipase of the pancreatic juice and proteolytic enzymes, viz., the pepsin of gastric juice, the trypsin of pancreatic juice, erepsin of the intestinal juice.
Thoroughly mixed with mucous in the buccal cavity, the food comes into the stomach. The parietal glands or the oxyntic cells in the mucous coat of stomach secrete hydrochloric acid. In the acidic medium, pepsin acts on proteins and converts them into peptones. After remaining for some time in the stomach, the half-digested acid chyme passes into the duodenum where it comes in contact with the bile.
Bile being alkaline neutralizes the acid. Trypsin then converts the peptones into the soluble amino acids which are readily absorbable. The erepsin of the intestinal juices quickens the process of conversion. Lipase converts fats into the soluble fatty acids and glycerol.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Amylase of pancreatic juice and the maltase of the intestinal juice convert fats into the soluble fatty acids and glycerol. The amylase of pancreatic juice and the maltase of the intestinal juice convert starch into glucose. The soluble food is absorbed and assimilated into the body and the indigestible products are egested as faeces through vent.
Spleen:
Spleen is a ductless glandular body of dark-red colour. It is spherical in shape and remains morphologically connected with the mesentery near the junction of the ileum and the rectum. Spleen acts as a storehouse of blood and also destroys old and worn out erythrocytes. It is believed that the leukocytes are manufactured in the spleen.