Learn about the comparison of skull in various vertebrates.
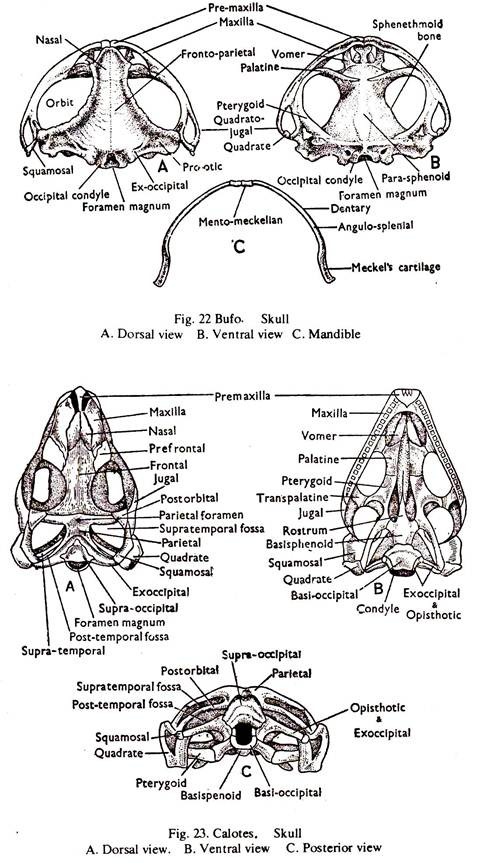
Comparison: Vertebrate # Bufo (Fig.22):
1. The back part of the skull bears a large hole posteriorly, the foramen magnum. The foramen is bounded by two exoccipitals at the sides, each bearing an occipital condyle.
Anteriorly, there is a cartilage bone, the sphenethmoid.
2. The roof of the cranium is formed by a pair of fronto-parietals and the floor by a dagger-shaped paraphenoid.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
3. The auditory capsule is ossified and consists of a single bone, the prootic. Behind the Otic Process a fenestra ovalis is present.
4. The nasal capsules are in front of the cranium and separated by the mesethmoid bone. They are roofed by two broad tapering nasals and floored by two vomers.
5. The upper jaw consists of two series of bones. The outer series of each side bears, premaxilla, maxilla and quadratojugals and the inner series of each side bears, a palatine, a pterygoid and a quadrate. A squamosal connects the otic capsule with the angle of the upper jaw.
6. The lower jaw consists of a pair of rods, the Meckel’s cartilages. The two cartilages are joined by ligament. The bones are dentary, angulosplenial and mentomeckelian cartilage bone.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
7. The sutures are distinct.
Comparison: Vertebrate # Calotes (Fig. 23):
1. The back part of the skull bears a large hole posteriorly, the foramen magnum. The foramen is bounded by two exoccipitals at the sides, the supraoccipital above and the basioccipital below which form the single condyle. The sphenethmoid is absent.
2. The roof of the cranium is formed by paired frontals and parietals. The parietals enclose a median hole, the parietal foramen. On each side, in front and behind the forntals are pre- and post-frontals. The floor is made of much reduced basis phenoid and parasphenoid.
3. The auditory capsule bears three ossification; prootic, epiotic and opisthotic. The exoccipital and the opisthotic bear horizontal processes, the parotic processes.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
4. The nasal capsules are roofed by a pair of nasals. A small lachrymal bone is present anteriorly in the orbit. The capsuels are separated by the mesethmoid bone.
5. The upper jaw consists of two series of bones. The outer series of each side bears, premaxilla, maxilla and the jugal, and the inner series of each side bears, the vomer, palatine, pterygoid, squamosal and the quadrate. The premaxilla and maxilla bear teeth.
6. The lower jaw consists of two rami. Each ramus consists of six bones, the articular, angular, supraangular, coronoid, splenial and dentary. The dentary bears teeth. The teeth are acrodont, that is they are solid and ankylosed to the upper part of the jaws.
7. The sutures are distinct.
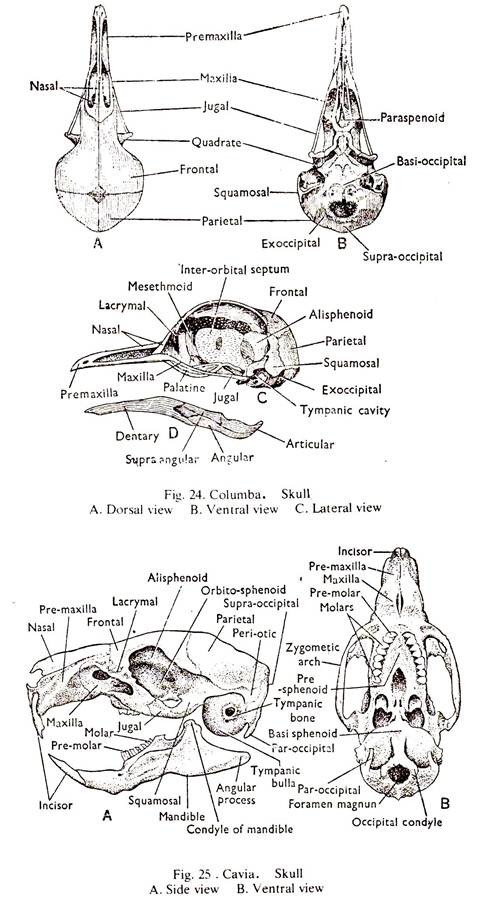
Comparison: Vertebrate # Columba (Fig.24):
1. The back part of the skull bears a large hole posteriorly, the foramen magnum. The foramen is bounded by two exoccipitals at the sides and the supraoccipital above and the basioccipital below, which mainly form the single condyle.
2. The roof of the cranium is formed by paired parietals and frontals. The floor is made of basisphenoid covered by a membrance bone, the basitemporal and the parasphenoid. Pre and post-frontals are absent.
3. The auditory capsule bears three ossifications; prootic, epiotic and opisthotic. The parotic processes are absent.
4. The nasal capsules are roofed by a pair of nasals. A lachrymal bone is present anteriorly and the posterior nares are between the palatines and the vomers. The capsules are separated by the mesethmoid bone Orbits are large.
5. The upper jaw consists of two series of bones. The palate is very imperfect. The outer series of each side bears, premaxilla, maxilla, jugal and the quadratojugal and the inner series bears, the vomer, palatine, pterygoid, squamosal and the quadrate. The voemr is vestigial. The teeth are absent. The quadrate movably articulates with the skull.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
6. The lower jaw consists of two rami. Each ramus bears the dentary, splenial, angular, supraaangular and the articular. The teeth are absent.
7. The sutures are completely obliterated.
Comparison: Vertebrate # Cavia (Fig. 25):
1. The back part of the skull bears a large holed posteriorly, the foramen magnum. The foramen is bounded by two exoccipitals at the sides forming the condyles, a supra occipital above and a basioccipital below. A paroccipital process descends from each exoccipital which is applied to the tympanic bulla.
2. The roof of the cranium is formed by paired parietals and frontals. The floor is made of basisphenoid, presphenoid and vomer, and the sides are made of quamosal, alisphenoid and orbitosphenoid.
3. The auditory capsule consists of mainly the periotic bone. The tubular portion of the tympanic bone surrounds the auditory meatus and its swollen portion forms the tympanic bulla. A zygomatic arch is formed on each side by the union of squamosal and jugal.
4. The olfactory capsule of each side is roofed by a narrow nasal. The outer and posteroior side is the formed bythe premaxilla and the vomers. A lachrymal bone is present between the frontal and the maxilla.
5. The upper jaw of each side consists of an anterior premaxilla and a posterior maxilla. They bear different types of socketed teeth. Incisor-1, premolar-1 and molar-3. A diastema is present (canine is absent).
6. The lower jaw consists of two rami. Each ramus is made of a single bone, the dentary, bearing socketed teeth like that of the upper jaw.
7. The sutures are distinct.
Comparison: Vertebrate # Canis:
The skull of dog is almost like that of a Cavia. Only the major points of differences are noted below.
1. The paroccipital process of the exoccipital is closely applied to the tympanic bulla.
2. An alisphenoid canal is present.
(a) A sagittal crest is present at the union of the parietals.
(b) The frontals carry postorbital processes.
3. The tympanic bulla is large.
(a) The jugal and the zygomatic arch are strong.
4. The nasals are well developed.
5. The dentition is
i (3/3). c (1/1). p (4/4). m (2/3) = 42
(a) Canines are powerful, pointed and project beyond other teeth.
(b) The last upper premolar and the first lower molar are modified for cutting (carnassial teeth).
(c) The crushing teeth behind the arnassials have broad crowns and bear four tubercles.
6. The mandible has a coronoid process and the glenoid articulation restricts the movement in vertical plane alone.