The following points highlight the top four modes of nutrition in protozoa. The modes are: 1. Holozoic 2. Holophytic (Holos = Whole + Phyton = Plant Origin) or Autotrophic (Photosynthesis) 3. Saprophytic (Sapros = Rotten) or Saprozoic 4. Parasitic.
Mode # 1. Holozoic:
(holos = whole + zoon = animal). Most of the free-living protozoon’s depend on engulfing the whole of the solid food particles. The food may be bacteria, protozoon’s or other small particles.
The food capturing devices are of the following types:
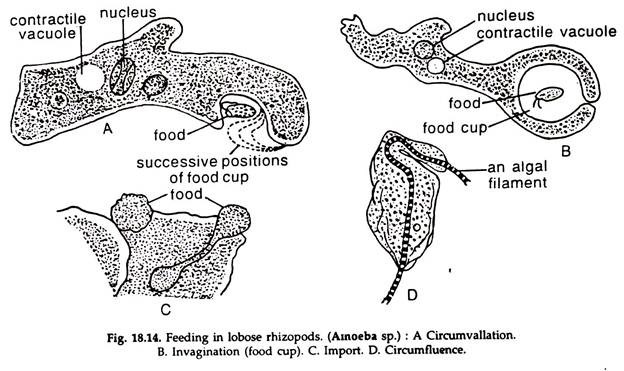
a. Circumvallation:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Encircling the active prey by pseudopodia. Example: Amoeba proteus (Fig. 18.14A).
b. Invagination:
The prey is immortile, food cup is formed and cytoplasm flows around to engulf it. Example: Amoeba dubia (Fig. 18.14B).
c. Import:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The prey is first killed by toxin and taken in the cytoplasm by invagination. Example: Amoeba sp. (Fig. 18.14C).
d. Circumfluence:
Food like algae is simply drawn into the body. Example: Amoeba sp. (Fig. 18.14D). The digestion mostly occurs in food vacuoles, in which acids or alkalis and digestive enzymes are secreted by the surrounding cytoplasm. Nutrients are absorbed by the cytoplasm and the undigested portion of the food in the vacuole is egested by repulsion (Amoeba), or through anal aperture or cytopyge (Paramoecium, Nyctotherus, etc.).
Mode # 2. Holophytic (Holos = Whole + Phyton = Plant Origin) or Autotrophic (Photosynthesis):
The chlorophyll-bearing flagellates or phytomastigophores synthesize carbohydrates from raw materials, water and carbon dioxide using radiant energy from the sun. Example: Euglena.
Mode # 3. Saprophytic (Sapros = Rotten) or Saprozoic:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Some protozoon’s cause disintegration of food materials into smaller molecules outside their body and subsist entirely on the dissolved organic matters. The monosaccharide’s, amino acids and other molecules are absorbed through the body surface. Examples: Entamoeba, histolytica, Gratium (a dinoflagellate), etc.
Mode # 4. Parasitic:
Parasitic protozoon’s are total or partial parasites in different organs of the hosts and obtain their food fully or partially from the organs. The parasites either rob the food of its host (Opalina, Gregarina, Nyctotherus, etc.) or feed upon the tissues of the hosts (Plasmodium, Entamoeba, etc.).