Learn about the comparison between external features of elasmobranch and teleost.
Comparison # External Features of Elasmobranch:
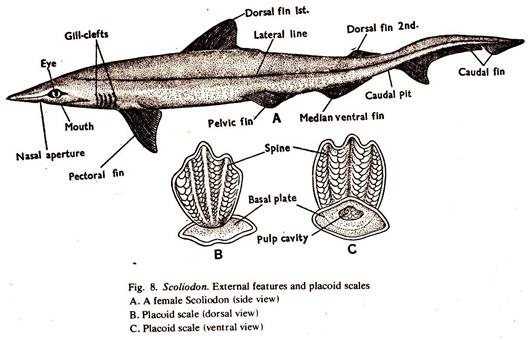
1. The mouth of Elasmobranch is ventral in position.
2. The body of Elasmobranch is covered with minute and microscopic placoid scales, the skin is tough.
3. Paired pelvic fins are provided with claspers in males.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
4. The tail of Elasmobranch is heterocercal, the vertebral column extending into the dorsal part of the caudal fin.
5. The head of Elasmobranch is dorsoventrally flattened.
6. Gill slits, usually five pairs, open separately and directly to the exterior.
7. The gills of Elasmobranch are hemibranch.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
8. Operculum are always absent in Elasmobranch.
9. A spiracle is usually present in Elasmobranch.
10. The endoskeleton is cartilaginous, with amphicoelous vertebrae.
11. A conus arteriosus is present. Aortic arches five pairs.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
12. A spiral or scroll valve is present in the intestine of Elasmobranch.
13. Stomach with distinct cardiac and pyloric regions. Intestinal caecum absent.
14. Elasmobranch are generally carnivorous, with a short intestine.
15. Gut with valves at all the junctions.
16. Cloaca is present in Elasmobranch.
17. An optic chiasma is present in Elasmobranch.
18. An air bladder is absent in Elasmobranch.
19. Gills with intrabranchial septum.
20. Testes are connected with the kidneys.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
21. Kidney elongated and narrow, with anterior non-renal and posterior renal portion.
22. The eggs are large and except one species provided with horny case.
23. In some cases, development takes place within the oviducts and the young ones are born alive.
24. In the embryo, gills project from the gill clefts as filaments.
25. Elasmobranch are marine.
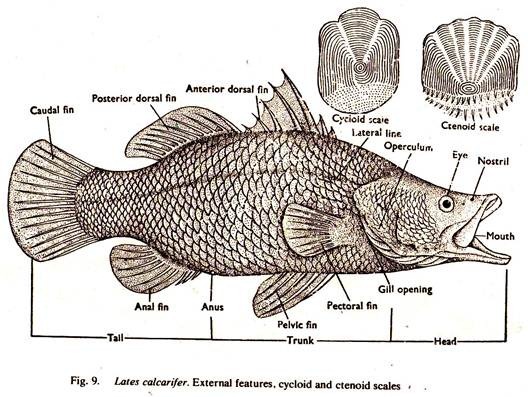
Comparison # External Features of Teleost (Fig. 9):
1. The mouth of Teleost is apical in position.
2. The body of Teleost is covered with cycloid or ctenoid or ganoid scales. The skin is soft. Complete absence of scales in cat fish group.
3. Claspers are absent in Teleost.
4. The tail of Teleost is homocercal, the vertebral column ends at the middle of the base of the caudal fin.
5. The head of Teleost may be dorsoventrally or laterally flattened.
6. Gill slits, usually four pairs, open in a gill chamber.
7. The gills of Teleost are holobranch.
8. Operculum with branchiostegal membrane always present.
9. A spiracle is absent in Teleost.
10. The endoskeleton is bony with amphicoelous vertebrae.
11. A conus arteriosus is absent. Aortic arches four pairs.
12. A spiral valve in the intestine is absent.
13. Stomach not differentiated into cardiac and pyloric portion. Intestinal caecum present.
14. Generally omnivorous, with a short or long intestine.
15. Valves few and far between.
16. Cloaca is absent in Teleost.
17. An optic chiasma is absent in Teleost.
18. An air bladder is usually present in Teleost.
19. Intrabranchial septum absent or rudimentary.
20. Testes are not connected with the kidneys.
21. Kidney fused, with a broad anterior and a narrow posterior portion.
22. The eggs are small but heavily yolked and without horny cases.
23. With a few exceptions, the young are hatched in an immature condition and undergo larval development.
24. Gill filaments remain covered by operculum.
25. Teleost are marine and fresh water forms.